CMMI for Acquisition — CMMI-ACQ
Introduction
CMMI-ACQ is part of the CMMI product family of process maturity models. It provides an opportunity for acquisition organisations
- to avoid or eliminate barriers and problems in the acquisition process through improved operational efficiencies
- to initiate and manage a process for acquiring products and services, including solicitations, supplier sourcing, supplier agreement development and award, and supplier capability management
- to utilize a common language for both acquirers and suppliers so that quality solutions are delivered more quickly and at a lower costs with the most appropriate technology
CMMI-ACQ was developed at the Software Engineering Institute (SEI) at Carnegie-Mellon University. It provides guidance for developing or improving processes that meet the business goals of an organisation.
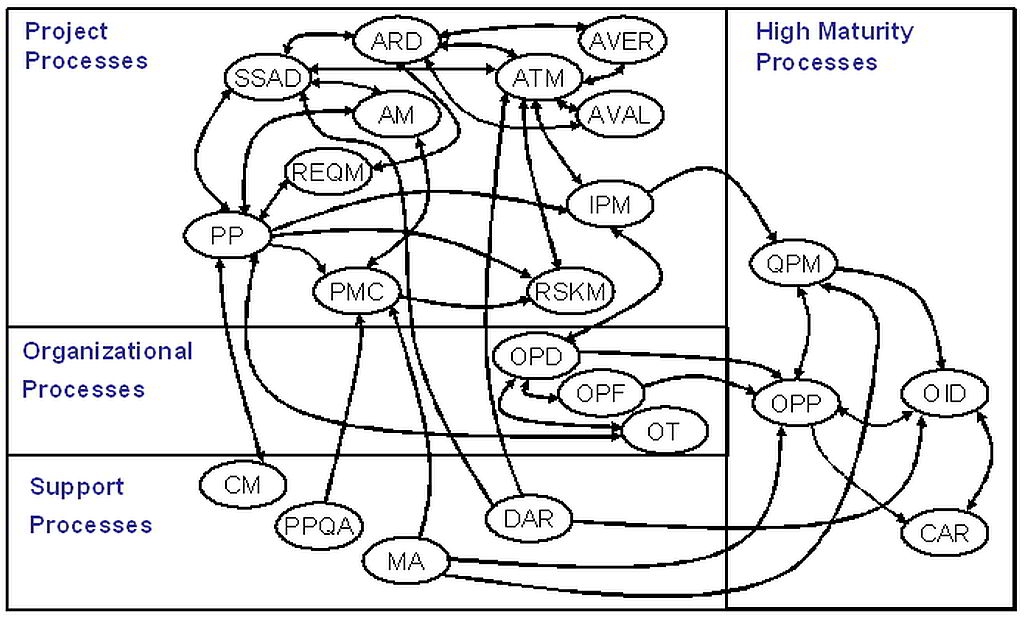
CMMI-ACQ Process Areas
CMMI-ACQ is a variant of the existing CMMI-DEV that shares much of the existing model (approximately 70% commonality) but with several critical differences designed to address the role of the Acquiring organisation.
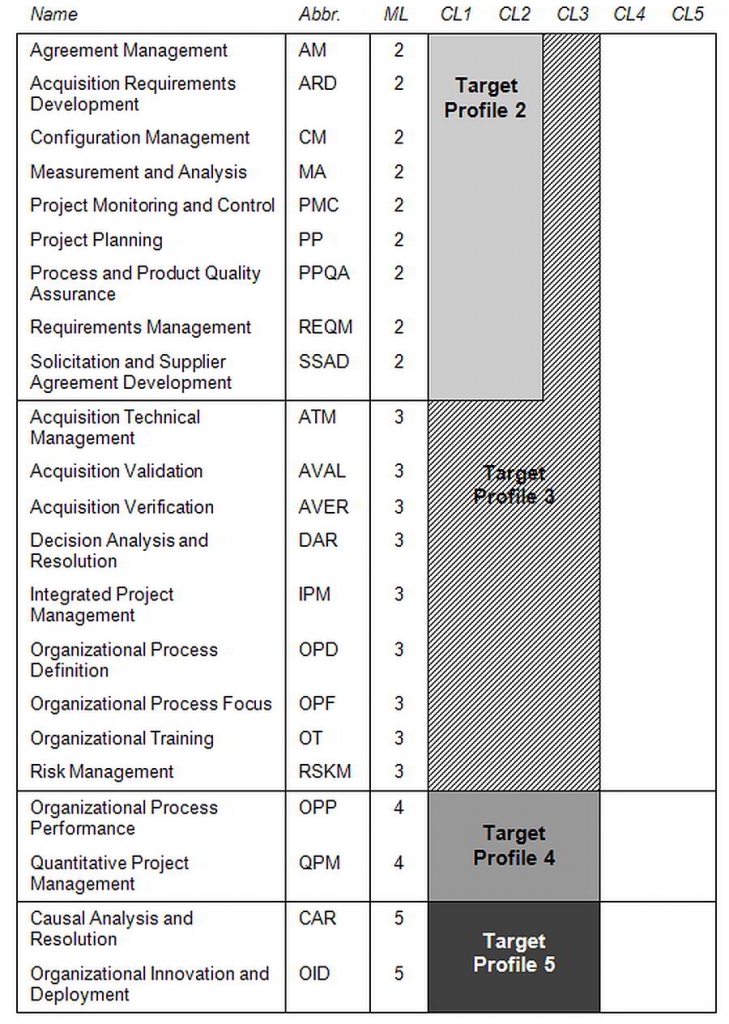
CMMI for Acquisition is based on the CMMI framework. The CMMI for Acquisition model has 22 process areas: six are specific to acquisition practices and sixteen are shared with other CMMI models.
The six process areas that are specific to acquisition are
- Acquisition Requirements Development (ARD) — elicit, develop, and analyze customer and contractual requirements.
- Solicitation and Supplier Agreement Development (SSAD) — prepare a solicitation package, select one or more suppliers to deliver the product or service, and establish and maintain the supplier agreement.
- Agreement Management (AM) — ensure that the supplier and the acquirer perform according to the terms of the supplier agreement.
- Acquisition Technical Management (ATM) — evaluate the supplier's technical solution and to manage selected interfaces of that solution.
- Acquisition Verification (AVER) — ensure that selected work products meet their specified requirements.
- Acquisition Validation (AVAL) — demonstrate that an acquired product or service fulfills its intended use when placed in its intended environment.
Additionally, the model includes guidance on
- Acquisition Strategy
- Typical Supplier Deliverables
- Transition to operations and support
- Teams and teaming
The sixteen shared process areas include practices for project management, organisational process management, and infrastructure and support.
Process Maturity Levels
As a CMMI model, it may also be used as a framework for appraising the process maturity of the organisation.
Further Readings
- CMMI-ACQ — SEI Homepage
- CMMI-ACQ — Model v.1.3 Download — PDF [3424 KB]
- CMMI-ACQ v1.3 — Quick Reference [PDF]
- CMMI-ACQ — Internet wiki
- Brian P. Gallagher, Mike Phillips, Karen Richter, Sandy Shrum:
(SEI Series in Software Engineering). Addison Wesley; 2nd revised edition. 2011.
- CMMI Product Team:
lulu.com, 2011.
: Elvert Barnes, via flickr.com • Christophe Guibert, via webideatree.com, .







Leave A Comment