Lean Change Canvas — How to Deliver Change Best
Lean Change Canvas
Very soon within the canvas family, the Lean Change Canvas by Jeff Anderson and Alexis Hui came up. Their Lean Change Method, adapts the ideas from Business Model Canvas (Alexander Osterwalder) and Lean Stack (Ash Maurya), and combines both with John Kotter's 8 Steps of Change.
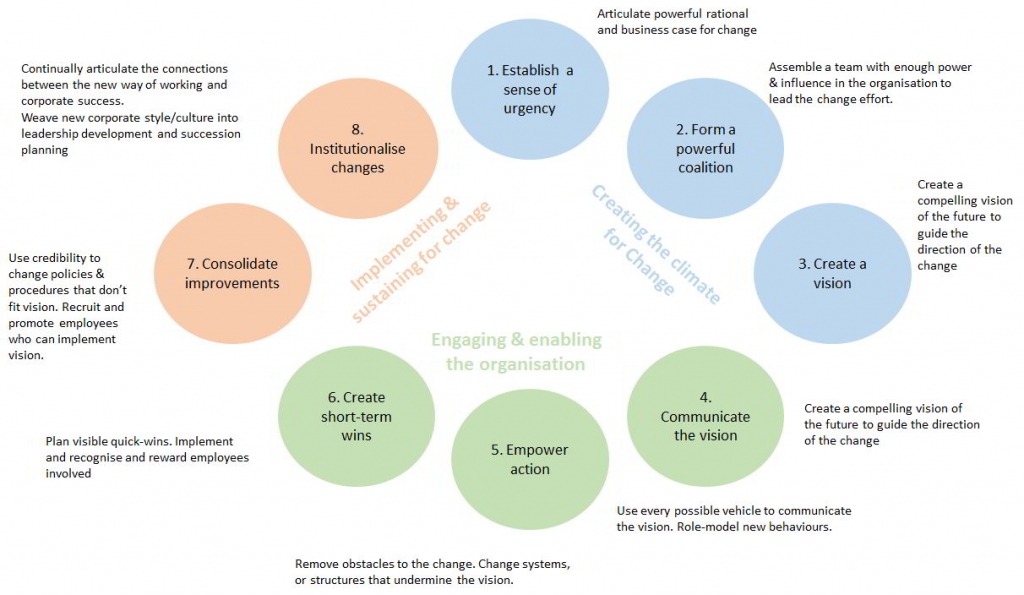
Eight Steps Leading Change
In 1996, John Kotter rocked the business world with his international bestseller, Leading Change. In this book, Kotter describes 8 leading steps fundamental to transform your organisation.
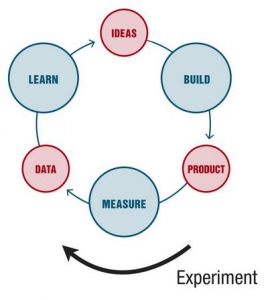
The Lean Stack approach is very empirical and highly data-driven. For all assumptions, risks and opportunities in your model, you define so-called "experiments":
"If we do X, we expect the result Y with an impact of Z"
You
- state a hypothesis
- develop a proving test environment for the hypothesis
- run the experiment for a certain time frame
- measure and collect data from running tests
- learn by interpreting the data
- rephrase the hypothesis and start a new experiment, if needed.
For example, before running a new marketing campaign, ground it with an empirical testable, i.e. measurable hypothesis like
"Customers at shop 42 Lincoln Avenue will accept higher prices if we explain them our fair trade policy."
Then, to validate the success of your marketing campaign, you set up an applicable test environment. You define suitable metrics and success criteria.
You run the campaign as "experiment" and collect data.
You interpret the data and accept whether your hypothesis is falsified or not.
If necessary, you change your hypothesis and start new experiments.
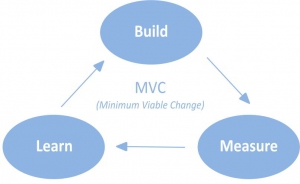
Minimum Viable Product and Minimum Viable Change
In (lean) product development, the minimum viable product (MVP) is the product with the highest return on investment versus risk. It has just those core features that allow the product to be deployed and to be used by a selected target group and no more.
The MVP is not necessarily the final product with all the features the customer wants. Of course, you do not find or create a minimum viable product in one big shot. Instead, you have to take many guesses ("hypothesis") what would make the success. You have to build many prototypes and test them as fast as possible on the market.
By running several MVPs you get a better understanding of the feature set of the final product the customer really wants. To put it short:
You continuously inspect and adapt your product (development).
In Lean product development, you regularly inspect and adapt by
- building prototypes ("hypothesis").
- testing them on the intended focus group ("measurement" = "inspect").
- improving your product/hypothesis ("adapt")
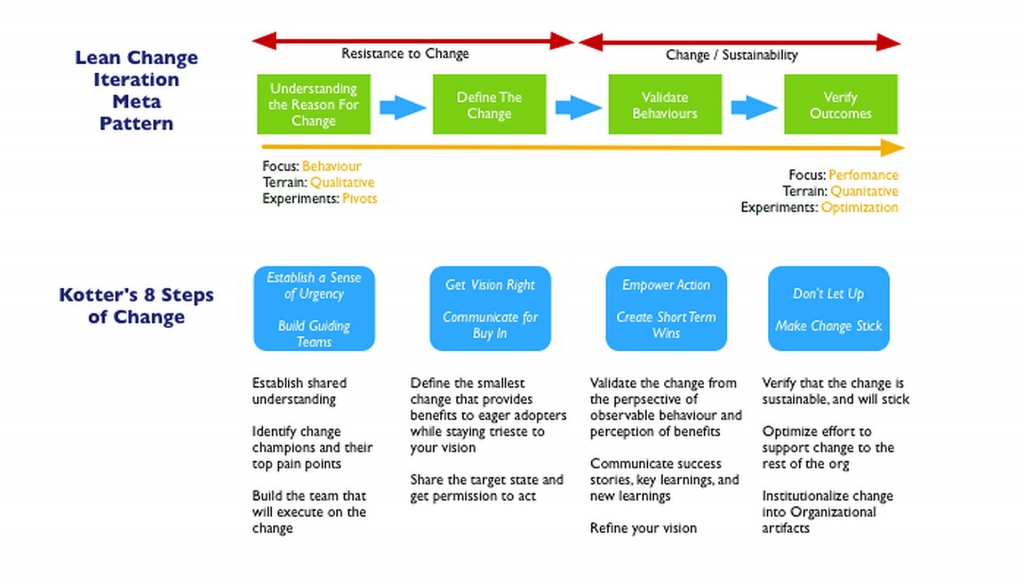
Lean Change and John Kotter
The "Lean Change Iteration Meta Pattern" reflects Kotter's 8 steps of leading change.
This pattern must be an integral part of every minimal viable change, you plan to deliver.
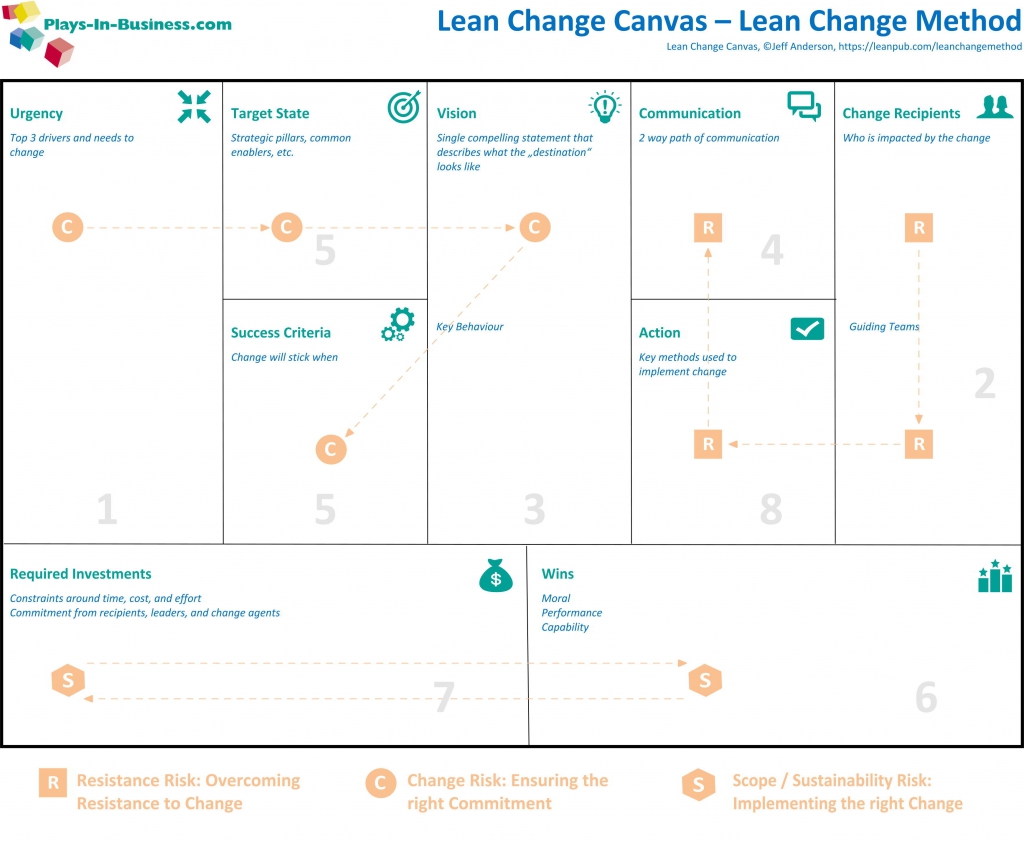
The Lean Change Canvas — Build The Blocks of Your Change Initiative
The Lean Change Canvas relates the typical canvas elements to organisational change context; maps each canvas element to one of Kotter's leading steps, identifies three risk classes, and proposes a certain work order for the quadrants.
Download your free Lean Change Canvas A0-Poster.
How To Use Lean Change Canvas
In general, there is no prescription in which order you have to have to fill the canvas' segments.
- Template:
- the canvas is a template to be used; print it on A0, A2, or A3 format ( Download your free Lean Change Canvas A0-Poster.) or use one of the available online formats.
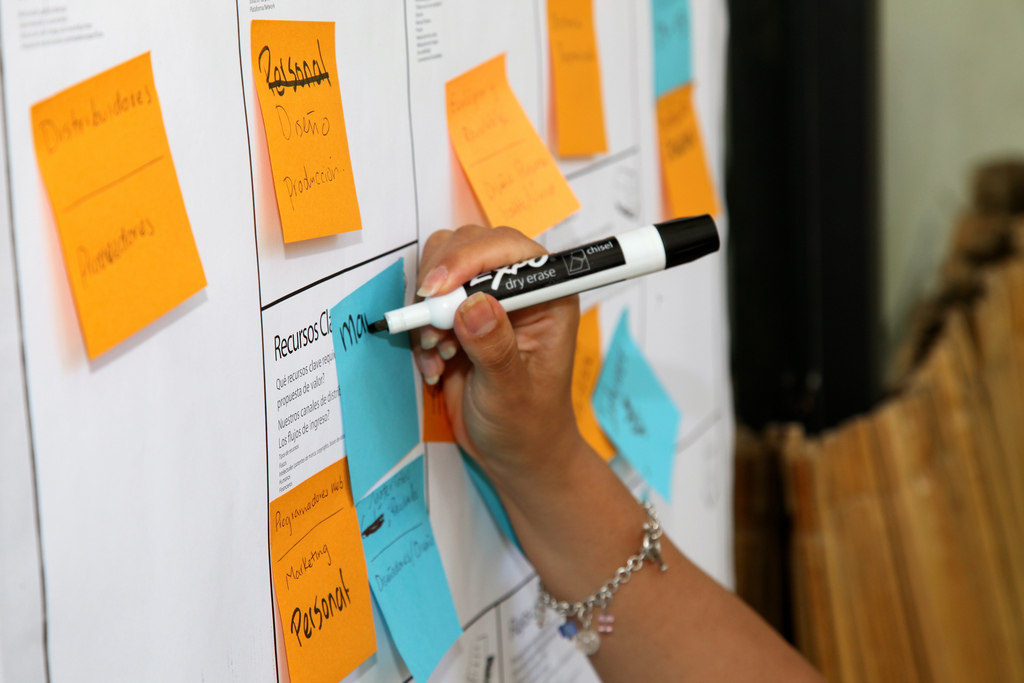
- Don't write on the canvas direct:
- use post-its instead — you can work more intuitively: One idea, one post-it.
- Use different coloured post-it:
- you can visualise different development stages or prioritisations. Besides of status-quo you can depict history and trade-offs of your change initiative.
- KISS 1:
- keep your canvas model as simple as possible: restrain yourself to short descriptions.
- KISS 2:
- Trying to design several models on the same canvas easily gets confusing:
- For each new business model use a separate canvas.
- Use different canvases for different customer segments if appropriate.
- Vizthinking:
- the canvas is a tool for visual thinking. Use product images and symbols instead of words.
- Scaling;
- the method scales easily: create groups of max 10 participants for large group facilitation.
- Working Left-to-right:
- when creating the canvas, start with the current situation and the intended goals and future state, because with the proper tuned mindset it is easier to proceed to left parts.
- Online Formats
- use the online formats when working with distributed teams.
Further Readings
Lean Change Method
- Lean Change Part 1 - Combining Kotter and Running Lean
- Lean Change Part 2 - The Lean Change Stack
- Think Visually When Building an Agile Enterprise Change Plan
- Jeff Anderson: Lean Change Method, (Book).
- Canvanizer: https://canvanizer.com/new/lean-change-canvas
Lean Stack
- Lean Stack (website)
- Ash Maurya: Running Lean: Iterate from Plan A to a Plan That Works, 2012
Kotter Steps of Change
- 8-Step Process for Leading Change (website)
- John Kotter: The Heart of Change: Real-Life Stories of How People Change Their Organisations, 2012.



Leave A Comment