CMMI for Services
CMMI for Services (CMMI-SVC) is part of the CMMI product family of process maturity models. It is a framework to guide organisations in improving their IT service delivery processes and to characterize the maturity of their IT operations. CMMI-SVC is an industry neutral model that can apply to any service industry.
CMMI-SVC sets up proven practices into a structure that helps an organisation to assess its organisational maturity and process area capability, establish priorities for improvement, and guide the process improvement initiative.
It is a compendium of proven practices which enables service-focused organisations to effectively
- …decide what services they should be providing, define standard services, and let people know about them
- …make sure they have everything they need to deliver a service, including people, processes, consumables, and equipment
- …make sure they have the resources needed to deliver services and that services are available when needed— at an appropriate cost
- …get new systems in place, change existing systems, retire obsolete systems, all while making sure nothing goes terribly wrong with the service
- …set up agreements, take care of service requests, and operate service systems
- …handle what goes wrong— and prevent it from going wrong in the first place if possible
- …ensure they are ready to recover from potential disasters and get back to delivering services if the disaster occurs
Going by the CMMI model definition: "Services are useful intangible and non-storable results delivered through a service system."
CMMI-SVC has synergies with models & standards like CMMI-DEV, ITIL, ISO/IEC 20000, CobiT and IT Service Continuity Management.
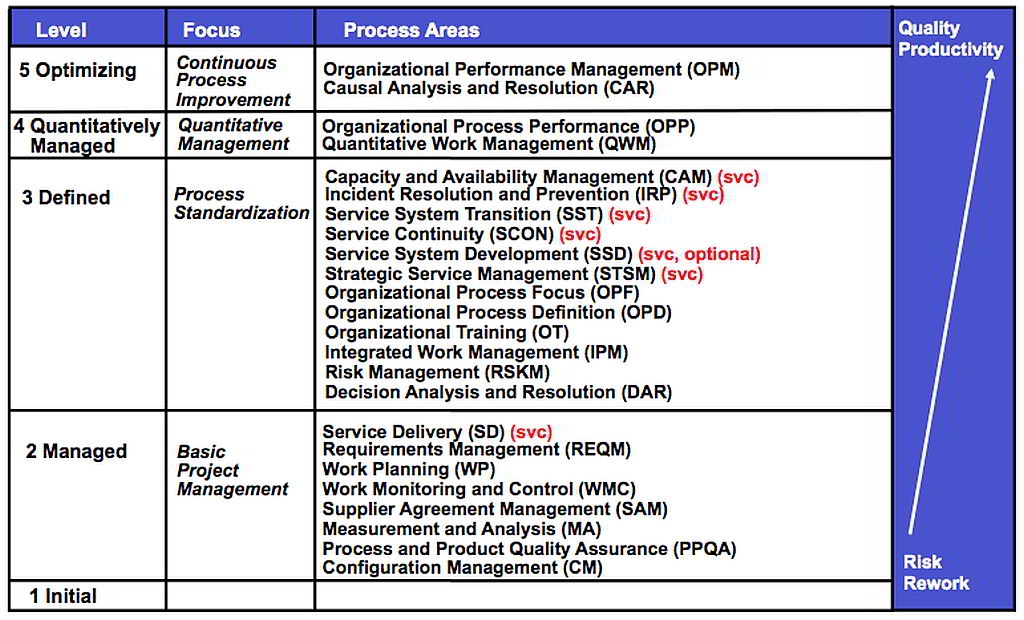
Process Areas of CMMI-SVC
- Capacity and Availability Management: Ensure effective service system performance and ensure that resources are provided and used effectively to support service requirements.
- Configuration Management: Establish and maintain the integrity of work products using configuration identification (labelling), configuration control (known modifications and permission to modify), configuration status accounting (final status of work products), and configuration audits (checks to verify changes).
- Decision Analysis and Resolution: Systematically select from alternative options using criteria, prioritization and an evaluation method.
- Incident Resolution and Prevention: Ensure timely and effective resolution of service incidents and prevention of service incidents as appropriate.
- Integrated Project Management: Perform work planning using company defined best practices and tailoring guidelines. Use organisational historical data for estimation. Identify dependencies and stakeholders for coordination, and comprehend this information into a master schedule or overall work plan.
As work progresses, coordinate all key stakeholders. Use thresholds to trigger corrective action (such as schedule and effort deviation metrics). - Measurement and Analysis: Develop and sustain a measurement capability that is used to support management information needs.
- Organisational Process Definition: Organize best practices and historical data into a useful and usable library.
- Organisational Process Focus: Coordinate improvements. Take what is learned at the team level and organize and deploy this information across the organisation. The result is that all teams improve faster from the positive and negative lessons of others.
- Organisational Training: Assess, prioritize and deploy training across the organisation, including domain-specific, technology and process skills needed to reduce errors and improve team efficiency.
- Process and Product Quality Assurance: Provide staff and management with objective insight into processes and associated work products.
- Requirements Management: a) Define the services of the group, b) trace defined services to team activities, c) verify that resources, service definition and actual work done match.
- Risk Management: Assess and prioritize all types of risks in a project and develop mitigation actions for the highest priority ones. Start by considering a predefined list of common risks and use a method for setting priorities.
- Service Continuity: Establish and maintain plans to ensure continuity of services during and following any significant disruption of normal operations.
- Service Delivery: Deliver services in accordance with service agreements. Prepare, execute and improve.
- Service System Development: Analyze, design, develop, integrate, verify, and validate service systems, including service system components, to satisfy existing or anticipated service agreements. [This is an optional Process Area.]
- Service System Transition: Deploy new or significantly changed service system components while managing their effect on ongoing service delivery.
- Strategic Service Management: Establish and maintain standard services in concert with strategic needs and plans.
The remaining Level 3 Process Areas are summarized below. - Supplier Agreement Management: Manage the acquisition of products and services from suppliers. This Process Area can be declared Not Applicable (after discussion with the appraiser) if there are no custom, risky, or integrated suppliers.
- The service-specific Process Areas are summarized below.
- Work Monitoring and Control: Understand the group’s progress so that appropriate corrective actions can be taken when performance deviates significantly from the plan.
- Work Planning: Establish and maintain plans (major tasks, estimates, risks and resources) for service work.
Process Maturity
Value of CMMI-SVC
- Rigorous yet flexible framework
- Improved Service Level Agreement compliance & delivery efficiency
- Improved customer satisfaction
- Optimised capacity utilization
- Effective change management
- Roadmap to service maturity
- Gain a marketing/competitive edge
Synergies with CMMI-DEV
- CMMI-SVC is an evolution from the earlier CMMI-DEV that have addressed Development as well as Acquisition of Products and Services. CMMI-SVC is focused on the delivery of Services.
- 16 of the 24 Process Areas come from the CMMI-DEV. For all constellations — the CMMI constellations give a common approach to implement many Project Management, Organisational Process Management and Supporting areas of work in an organisation.
- CMMI-SVC is also supported by the SCAMPI appraisal methodologies.
Further Readings
- CMMI-SVC — SEI Homepage
- CMMI-SVC — Model v.1.3 Download — PDF [4215 KB]
- CMMI-SVC v.1.3 — Quick Reference - [PDF]
- Maturity Levels 2 & 3. Goals And Practices - [PDF]
- Eileen C. Forrester, Brandon L. Buteau, Sandy Shrum:
(SEI Series in Software Engineering), Addison Wesley; Auflage: 2nd revised edition, 2011.
- CMMI Product Team:
lulu.com, 2011.
- Christian Hertneck, Ralf Kneuper:
. dpunkt Verlag; Juni 2011.







Interesting, very good article!!